Modbus RTU Communication is used for communication between PLC and other devices with supporting modbus communication. Example modbus communication between PLC and Computer, PLC and Android, PLC and Arduino, PLC and PLC, PLC and CNC, PLC and Robot, and others.
In this article, I give an example: a simple way the use modbus communication between PLC and Computer/PC by using Microsoft Visual C# (C Sharp).
A. Modbus Master and Modbus Slave
In modbus communication, must first determine modbus master and modbus slave.
See the image below:
1. PC/Computer, CNC defined as Modbus Master
2. PLC defined as Modbus Slave
Modbus Master is a device Request the Data and write Data to the Modbus Slaves.
Modbus Slave is some devices Response Data to Modbus Master.
One Modbus Master can be connected up to 247 Modbus Slaves.
Each Modbus Slaves has a Unique Address/ID from 1 to 247.
Some PLCs that can be used as a Modbus Slave: Modicon PLC,Siemens PLC, Allen Bradley PLC, and Others.
For testing, I use Siemens PLC S7-200.
B. Modbus Function Code
For communicate between modbus master and modbus slave using modbus protocol, modbus protocol have some code and its function.
The listing below shows the modbus codes supported by Modicon:
I use function code 03 and function code 16 for modbus testing and this function code that is most commonly used in general. For another function code please try yourself, download the complete modbus protocol, click here
C. Function Code 03 of ModBus
Function Code 03 is used for Reads the binary contents of Holding Registers in the address range of 40000 to 49999 and usually called 4x.
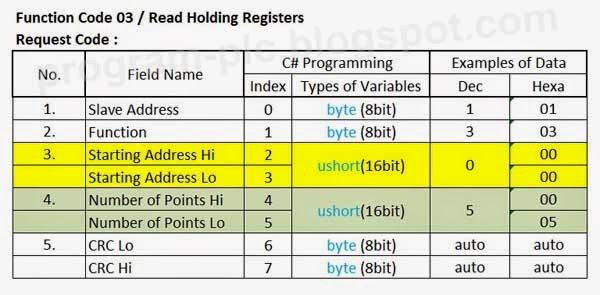
Parameters of Function Code 03 / Read Holding Registers:
Request/Query of Modbus Master:
Example: I want to read registers from starting address 0 in modbus slave with address 1, and the number of registers (number of points) read as 5 registers.
The request code is:
Request/Query in C# Programming:
Supply/Response of Modbus Slave with address 1:
Read Registers Data from Response in C# Programming:
The registers data starting from index 3.
D. Function Code 16 of ModBus
Parameters of Function Code 16 / Preset Multiple Registers:
Request/Query of Modbus Master:
Example: I want to write values to registers from starting address 5 in modbus slave with address 1, and the number of registers is written as 2 registers.
The request code is:
Request/Query in C# Programming:
Supply/Response of Modbus Slave with address 1:
For Response at the Modbus Function Code 16, should use the CRC Checker.
CRC (Cyclical Redundancy Check) Checker in C# Programming:
E. Read/Write Registers in PLC Siemens S7-200 with Modbus Function Code 03 and 16
In PLC S7-200, I use Registers VB800 as Starting Address in Modbus.
See Ladder programming, and a list of tables registers:
Siemens S7-200 Modbus
ModBus Registers in Siemens PLC S7-200
F. Project File
1. Download project file for Microsoft Visual C#, click here
2. Download PLC Ladder Programming for Siemens PLC S7-200, click here
See video about Testing of Modbus: Function Code 03
See video about Testing of Modbus: Function Code 16
Thank you for reading my article and have been watching my videos, and always visit my blog in the next day.
In this article, I give an example: a simple way the use modbus communication between PLC and Computer/PC by using Microsoft Visual C# (C Sharp).
A. Modbus Master and Modbus Slave
In modbus communication, must first determine modbus master and modbus slave.
See the image below:
1. PC/Computer, CNC defined as Modbus Master
2. PLC defined as Modbus Slave
Modbus Master is a device Request the Data and write Data to the Modbus Slaves.
Modbus Slave is some devices Response Data to Modbus Master.
One Modbus Master can be connected up to 247 Modbus Slaves.
Each Modbus Slaves has a Unique Address/ID from 1 to 247.
Some PLCs that can be used as a Modbus Slave: Modicon PLC,Siemens PLC, Allen Bradley PLC, and Others.
For testing, I use Siemens PLC S7-200.
B. Modbus Function Code
For communicate between modbus master and modbus slave using modbus protocol, modbus protocol have some code and its function.
The listing below shows the modbus codes supported by Modicon:
I use function code 03 and function code 16 for modbus testing and this function code that is most commonly used in general. For another function code please try yourself, download the complete modbus protocol, click here
C. Function Code 03 of ModBus
Function Code 03 is used for Reads the binary contents of Holding Registers in the address range of 40000 to 49999 and usually called 4x.
Parameters of Function Code 03 / Read Holding Registers:
Request/Query of Modbus Master:
Example: I want to read registers from starting address 0 in modbus slave with address 1, and the number of registers (number of points) read as 5 registers.
The request code is:
Request/Query in C# Programming:
//Function 3
request is always 8 bytes= index0 to index7
byte[] message = new byte[8];
byte
Slave_Address = 1;
byte Function =
3;
ushort
Starting_Address = 0;
ushort
Number_of_Points = 5;
//index0 = Slave
Address
message[0] = Slave_Address;
//index1 =
Function
message[1] = Function;
//index2 =
Starting Address Hi
message[2] = (byte)(Starting_Address >> 8);
//index3 =
Starting Address Lo
message[3] = (byte)Starting_Address;
//index4 = Number
of Points Hi
message[4] = (byte)(Number_of_Points >> 8);
//index5 = Number
of Points Lo
message[5] = (byte)Number_of_Points;
// CRC (Cyclical
Redundancy Check) Calculation
ushort CRC =
0xFFFF;
byte CRCHi =
0xFF;
byte CRCLo =
0xFF;
ushort CRCLSB;
for (int i = 0; i < (message.Length) - 2; i++)
{
CRC = (ushort)(CRC
^ message[i]);
for (int
j = 0; j < 8; j++)
{
CRCLSB = (ushort)(CRC
& 0x0001);
CRC = (ushort)((CRC
>> 1) & 0x7FFF);
if (CRCLSB == 1)
CRC = (ushort)(CRC
^ 0xA001);
}
}
CRCHi = (byte)((CRC >> 8) & 0xFF);
CRCLo = (byte)(CRC & 0xFF);
//index6 = CRC Lo
message[message.Length - 2] =
CRCLo;
//index7 = CRC Hi
message[message.Length - 1] =
CRCHi;
Read Registers Data from Response in C# Programming:
The registers data starting from index 3.
//Byte Count in
index 3 = responseFunc3[2]
//Number of
Registers = byte count / 2 = responseFunc3[2] / 2
byte registers =
(byte)(responseFunc3[2] / 2);
short[] values = new short[registers];
for (int i = 0; i < registers; i++)
{
//Data Hi of
Registers1 from Index3
values[i] = responseFunc3[2 *
i + 3];
//Move to Hi
values[i] <<= 8;
//Data Lo of
Registers1 from Index4
//Registers data
is Data Hi + Data Lo
values[i] += responseFunc3[2 *
i + 4];
}
Parameters of Function Code 16 / Preset Multiple Registers:
Request/Query of Modbus Master:
Example: I want to write values to registers from starting address 5 in modbus slave with address 1, and the number of registers is written as 2 registers.
The request code is:
Request/Query in C# Programming:
//index0 = Slave
Address
message[0] = Slave_Address;
//index1 =
Function
message[1] = Function;
//index2 =
Starting Address Hi
message[2] = (byte)(Starting_Address >> 8);
//index3 =
Starting Address Lo
message[3] = (byte)Starting_Address;
//index4 = Number
of Registers Hi
message[4] = (byte)(NumberofRegisters >> 8);
//index5 = Number
of Registers Lo
message[5] = (byte)NumberofRegisters;
//index6 = Byte
Count
message[6] = Byte_Count;
for (int i = 0; i < NumberofRegisters; i++)
{
//Data Hi, index7
and index9
message[7 + 2 * i] = (byte)(values[i] >> 8);
//Data Lo, index8
and index10
message[8 + 2 * i] = (byte)(values[i]);
}
// CRC (Cyclical
Redundancy Check) Calculation
ushort CRC =
0xFFFF;
byte CRCHi =
0xFF;
byte CRCLo =
0xFF;
ushort CRCLSB;
for (int i = 0; i < (message.Length) - 2; i++)
{
CRC = (ushort)(CRC
^ message[i]);
for (int
j = 0; j < 8; j++)
{
CRCLSB = (ushort)(CRC
& 0x0001);
CRC = (ushort)((CRC
>> 1) & 0x7FFF);
if (CRCLSB == 1)
CRC = (ushort)(CRC
^ 0xA001);
}
}
CRCHi = (byte)((CRC >> 8) & 0xFF);
CRCLo = (byte)(CRC & 0xFF);
//index11= CRC Lo
message[message.Length - 2] =
CRCLo;
//index12 = CRC Hi
message[message.Length - 1] =
CRCHi;
For Response at the Modbus Function Code 16, should use the CRC Checker.
CRC (Cyclical Redundancy Check) Checker in C# Programming:
private bool CRCResponseCheck(byte[]
message)
{
//CRC Response
Check:
byte[] CRC = new byte[2];
ushort CRCFull =
0xFFFF;
byte CRCHigh =
0xFF, CRCLow = 0xFF;
ushort CRCLSB;
for (int i = 0; i < (message.Length) - 2; i++)
{
CRCFull = (ushort)(CRCFull
^ message[i]);
for (int
j = 0; j < 8; j++)
{
CRCLSB = (ushort)(CRCFull
& 0x0001);
CRCFull = (ushort)((CRCFull
>> 1) & 0x7FFF);
if (CRCLSB == 1)
CRCFull = (ushort)(CRCFull
^ 0xA001);
}
}
CRCHigh = (byte)((CRCFull >> 8) & 0xFF);
CRCLow = (byte)(CRCFull & 0xFF);
if (CRCLow ==
message[message.Length - 2] && CRCHigh == message[message.Length - 1])
return true;
else
return false;
}
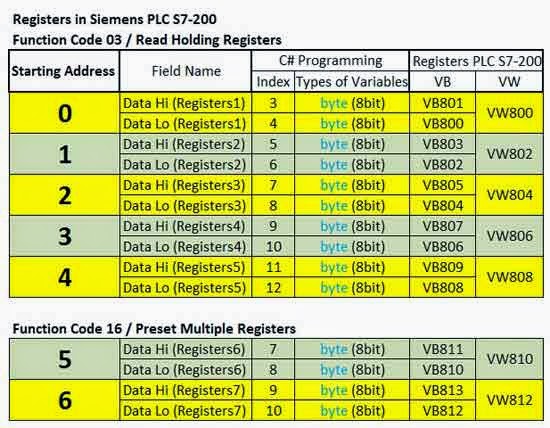
In PLC S7-200, I use Registers VB800 as Starting Address in Modbus.
See Ladder programming, and a list of tables registers:
Siemens S7-200 Modbus
ModBus Registers in Siemens PLC S7-200
F. Project File
1. Download project file for Microsoft Visual C#, click here
2. Download PLC Ladder Programming for Siemens PLC S7-200, click here
See video about Testing of Modbus: Function Code 03
See video about Testing of Modbus: Function Code 16
Thank you for reading my article and have been watching my videos, and always visit my blog in the next day.
Labels:
Modbus
ModBus Communication
ModBus RTU
ModBus RTU Communication
PLC Application
Simple ModBus
Modbus
ModBus Communication
ModBus RTU
ModBus RTU Communication
PLC Application
Simple ModBus